The Future of Nuclear Weapons: Assessing Proliferation and US Response

The Future of Nuclear Weapons: Assessing the Threat of Proliferation and the US Response involves analyzing current geopolitical tensions, technological advancements, and international agreements to understand how nuclear arsenals might evolve and what strategies the United States can employ to mitigate risks and maintain global security.
The specter of nuclear war has haunted humanity for decades. Today, with evolving geopolitical landscapes and technological advancements, understanding the Future of Nuclear Weapons: Assessing the Threat of Proliferation and the US Response is more critical than ever.
Understanding the Current Nuclear Landscape
To effectively assess the future of nuclear weapons, we must first understand the present state of affairs. This includes an overview of existing nuclear arsenals, the nations that possess them, and the treaties and agreements designed to limit their spread.
Existing Nuclear Arsenals
Currently, a handful of nations possess nuclear weapons, with the United States and Russia holding the largest stockpiles. Understanding the size and composition of these arsenals is crucial for assessing potential threats.
Key Nuclear Weapon States
Besides the US and Russia, countries like China, France, the United Kingdom, Pakistan, India, Israel, and North Korea possess nuclear capabilities. Each nation has its own strategic rationale for maintaining or developing these weapons.
- United States: Maintains a triad of land-based missiles, submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and strategic bombers.
- Russia: Similar to the US, with a focus on modernizing its nuclear forces.
- China: Rapidly expanding its nuclear arsenal with a focus on diversification.
- North Korea: Continues to develop nuclear weapons despite international sanctions.
The current nuclear landscape is complex, with varying levels of commitment to arms control and non-proliferation from different nations. This complexity is a significant factor in shaping the future of nuclear weapons.
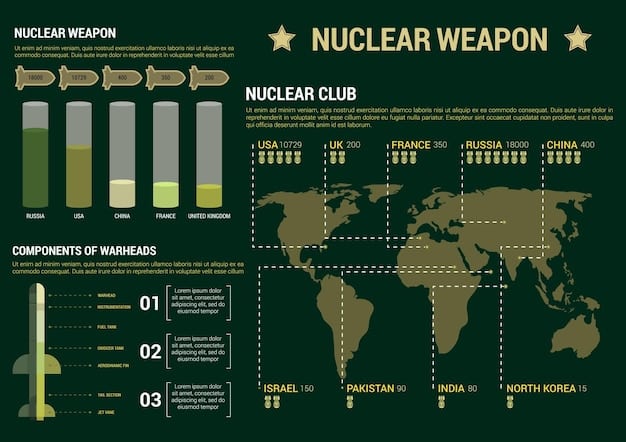
In conclusion, the existing nuclear landscape is characterized by a handful of nations possessing varying levels of nuclear capabilities. Understanding the arsenals and strategic postures of these nations is essential for addressing the challenges of nuclear proliferation and maintaining global security.
The Threat of Nuclear Proliferation
One of the most pressing concerns regarding the future of nuclear weapons is the potential for further proliferation. This involves both state and non-state actors acquiring nuclear weapons or the capability to produce them.
Factors Driving Proliferation
Several factors contribute to the risk of nuclear proliferation, including regional conflicts, security dilemmas, and the pursuit of prestige or strategic advantage.
State Actors and Proliferation Risks
Certain states are of particular concern due to their political instability, ongoing conflicts, or history of pursuing nuclear weapons. Monitoring these states is crucial for preventing proliferation.
- Iran: Its nuclear program remains a major concern, with ongoing negotiations aimed at preventing the development of nuclear weapons.
- North Korea: Continues to defy international pressure and expand its nuclear capabilities.
- Saudi Arabia: There are concerns that Saudi Arabia might seek nuclear weapons if Iran acquires them.
Non-State Actors and Nuclear Terrorism
The possibility of a terrorist group acquiring or developing nuclear weapons is a grave concern. This scenario could lead to catastrophic consequences and requires robust preventative measures.
The threat of nuclear proliferation is a complex issue driven by a variety of factors. Preventing proliferation requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying causes and strengthens international safeguards.
US Nuclear Deterrence Strategy
The United States relies on a strategy of nuclear deterrence to prevent attacks on itself and its allies. This strategy involves maintaining a credible nuclear arsenal and communicating the willingness to use it in response to aggression.
The concept of deterrence
Deterrence is based on the principle that a potential adversary will be dissuaded from attacking if they believe the retaliation will be too costly. This requires maintaining a credible and capable nuclear force.
Maintaining a credible nuclear arsenal
Ensuring the credibility of the US nuclear deterrent involves modernizing existing weapons, developing new capabilities, and maintaining a robust command and control system.
The nuclear triad
A critical component of the US nuclear deterrent is the nuclear triad, which consists of land-based missiles, submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and strategic bombers. This provides redundancy and ensures the ability to retaliate even if one leg of the triad is compromised.
- Land-Based Missiles (ICBMs): Offer quick response times and high accuracy.
- Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs): Provide a survivable and undetectable deterrent.
- Strategic Bombers: Offer flexibility and the ability to demonstrate resolve.
The US nuclear deterrence strategy is designed to prevent nuclear attacks by convincing potential adversaries that the costs of aggression far outweigh the benefits. Maintaining a credible and capable nuclear force is essential for this strategy to succeed.
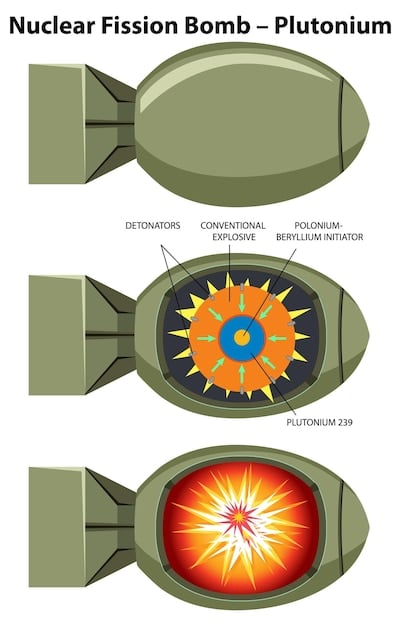
In summary, the US nuclear deterrence strategy is a cornerstone of national security, relying on a credible and capable nuclear force to prevent attacks. The nuclear triad provides redundancy and ensures the ability to retaliate, maintaining stability in a complex geopolitical environment.
Arms Control and Non-Proliferation Efforts
In addition to nuclear deterrence, arms control and non-proliferation efforts play a crucial role in reducing the risk of nuclear war. These efforts involve treaties, agreements, and international organizations working to limit the spread of nuclear weapons.
The Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT)
The NPT is a landmark treaty aimed at preventing the spread of nuclear weapons and promoting disarmament. It has been signed by most countries in the world and forms the basis of the international non-proliferation regime.
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
The IAEA plays a critical role in verifying compliance with the NPT and providing technical assistance to countries seeking to develop nuclear energy for peaceful purposes. Its safeguards are essential for detecting and preventing the diversion of nuclear materials.
Challenges to Arms Control
Despite the successes of arms control efforts, there are significant challenges. These include non-compliance, the development of new weapons technologies, and geopolitical tensions that undermine cooperation.
- Non-Compliance: Some countries have been accused of violating arms control agreements.
- New Technologies: The development of hypersonic missiles and autonomous weapons systems poses new challenges to arms control.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Rising tensions between major powers can undermine cooperation on arms control.
Arms control and non-proliferation efforts are essential for reducing the risk of nuclear war. These efforts require international cooperation, strong verification mechanisms, and a commitment to addressing the underlying causes of proliferation.
In conclusion, arms control and non-proliferation efforts, spearheaded by treaties such as the NPT and organizations like the IAEA, are vital for reducing nuclear risks. Addressing the challenges to these efforts requires ongoing international cooperation and a commitment to disarmament.
Technological Advancements and Nuclear Weapons
Technological advancements are profoundly impacting the future of nuclear weapons. New delivery systems, warhead designs, and detection technologies are changing the strategic landscape and posing new challenges for arms control.
New Delivery Systems
The development of hypersonic missiles and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is creating new challenges for missile defense systems and arms control efforts. These systems can deliver nuclear weapons with greater speed and maneuverability.
Warhead Design
Advancements in warhead design are leading to smaller, more accurate, and more versatile nuclear weapons. This can increase the risk of their use in regional conflicts or by non-state actors.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Nuclear Weapons
The integration of AI into nuclear weapons systems raises concerns about the potential for errors, miscalculations, and unintended escalation. Autonomous weapons systems could make decisions without human intervention, increasing the risk of accidental war.
- Hypersonic Missiles: Can evade missile defenses due to their speed and maneuverability.
- Smaller Warheads: Easier to transport and conceal, increasing the risk of proliferation.
- AI Integration: Could lead to unintended escalation and accidental war.
Technological advancements are transforming the nuclear landscape, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Managing these changes requires careful consideration of the ethical, strategic, and arms control implications.
In sum, technological advancements in delivery systems, warhead design, and AI integration are reshaping the future of nuclear weapons. Addressing the challenges posed by these advancements requires proactive arms control measures and careful consideration of the strategic implications.
Diplomacy and International Relations
Diplomacy and international relations play a crucial role in shaping the future of nuclear weapons. Effective communication, negotiation, and conflict resolution are essential for reducing tensions and preventing nuclear war.
The Role of Diplomacy
Diplomacy provides a forum for countries to address their concerns, negotiate agreements, and build trust. It is an essential tool for managing conflicts and preventing escalation.
Bilateral and Multilateral Negotiations
Bilateral negotiations between major powers, such as the US and Russia, are crucial for reducing nuclear arsenals and limiting strategic competition. Multilateral negotiations, such as those involving the Iran nuclear deal, can address specific proliferation risks.
Conflict Resolution and Crisis Management
Effective conflict resolution and crisis management mechanisms are essential for preventing nuclear war in the event of a crisis. This requires clear communication channels, agreed-upon rules of engagement, and a willingness to compromise.
- Effective Communication: Clear and reliable communication channels are essential for preventing misunderstandings and miscalculations.
- Negotiation Skills: Skilled negotiators can find common ground and reach agreements that address the concerns of all parties.
- Crisis Management: Effective crisis management mechanisms can prevent escalation and de-escalate tensions.
Diplomacy and international relations are essential for managing the risks posed by nuclear weapons. These efforts require a commitment to dialogue, negotiation, and peaceful conflict resolution.
In conclusion, diplomacy and international relations are critical for shaping a safer future regarding nuclear weapons. Effective bilateral and multilateral negotiations, coupled with robust conflict resolution mechanisms, are essential for reducing tensions and preventing nuclear war.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| ☢️ Nuclear Arsenals | Understanding the size and distribution of current nuclear stockpiles. |
| 🌍 Proliferation Risks | Assessing the dangers of nuclear weapons spreading to more countries or groups. |
| 🛡️ Deterrence Strategy | How the US aims to prevent nuclear attacks through a strong deterrent. |
| 🤝 Arms Control | International efforts to limit and reduce nuclear weapons. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
The countries known to possess nuclear weapons are the United States, Russia, China, France, the United Kingdom, Pakistan, India, Israel, and North Korea. These nations vary significantly in the size and sophistication of their nuclear arsenals.
▼
Nuclear deterrence is a strategy where a nation maintains a powerful nuclear arsenal to discourage other countries from attacking it. The idea is that the potential for devastating retaliation will prevent any first strike.
▼
The NPT is an international treaty created to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and promote disarmament. It requires countries without nuclear weapons to not acquire them and mandates nuclear-weapon states to work towards disarmament.
▼
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is responsible for promoting the safe, secure, and peaceful use of nuclear technology. It verifies that nuclear materials are not diverted for weapons purposes and helps countries improve nuclear safety.
▼
AI could lead to more autonomous nuclear weapon systems, increasing the risk of unintended escalation. These systems might make decisions without human intervention, leading to errors and miscalculations. This is a developing and concerning area.
Conclusion
The future of nuclear weapons remains uncertain, with trends pointing to increased risks of proliferation and the emergence of new technological challenges. Addressing these threats requires a multi-faceted approach that combines robust deterrence, proactive arms control efforts, and sustained diplomatic engagement to ensure global security. Navigating this landscape will be crucial for the US and the international community in the years to come.





